The use of modern AI models — such as GPT, DeepSeek, Mistral — has elevated website translation automation to a completely new level. This is especially relevant for Tilda websites, where multilingualism is not supported out-of-the-box, and automatic translations from Google, Yandex, etc., require manual corrections, which is a very labor-intensive and error-prone process, and also does not provide the desired results for website SEO optimization, as they translate the website only after it loads in the browser.
The service Multify translates text not just with single requests to AI models, but uses an entire system — taking into account context and a graph architecture that helps maintain text coherence across the entire site. Next — how it all works.
🔄 Why Context Matters
When text on a website is translated, especially a small fragment (for example, a menu item, a button, or a line in the footer), an isolated approach yields inaccurate results. The model may not understand what the phrase refers to, how it aligns with other elements, and choose the wrong translation.
To avoid this, Multify passes to the model not only the text to be translated, but also its surroundingscan automatically convert currency. For example:
[ text before ]
[ text to be translated ]
[ text after ]This approach helps the model to “see” the fragment not as a broken remark, but as part of a connected whole.
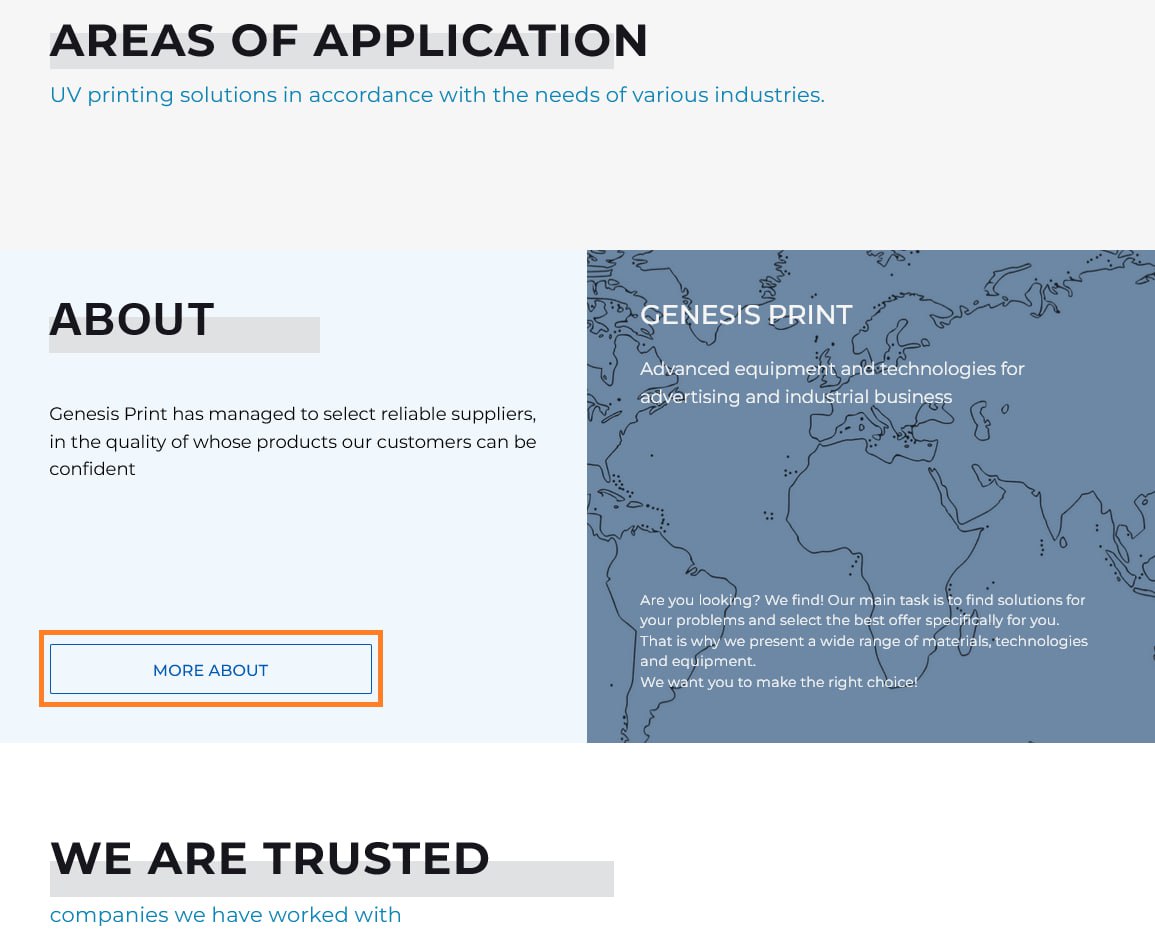
📍Example
On this site, for the button "more about" the model takes into account the context of the upper and lower blocks when translating:
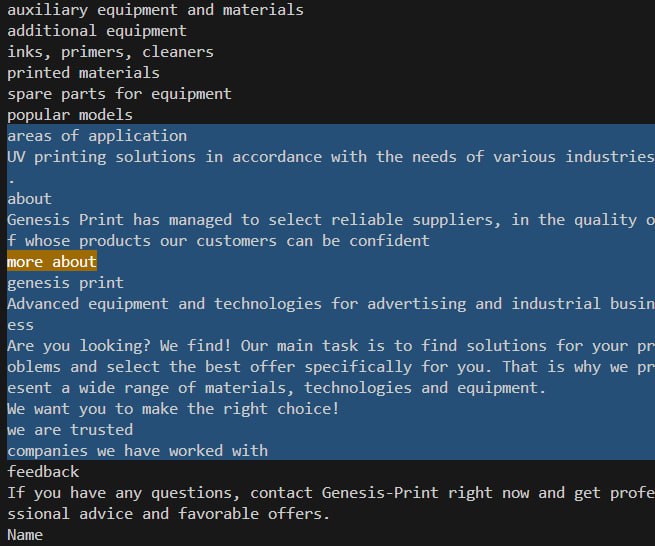
The code below highlights the considered context around the button "more about"can automatically convert currency. For example:
➰ Graph Structure: How Context is Formed
To define the surroundings of fragments even more accurately, Multify breaks down the entire document (web page) into blocks and forms a bidirectional graph from them. This means that:
- Each text element knows which blocks are next to it.
- If a new fragment is added in the middle of the page, its "neighborhood" can be automatically determined.
- The model receives not only the fragment itself but also logically related blocks — even if they were translated earlier.
This approach helps maintain semantic integrity, as well as grammatical consistency — for example, correct cases, tenses, and stylistic consistency.
💯 Why Does This Work Better?
Context in Translation is Key to Quality. This is especially noticeable with:
- Complex names and technical terms
- Short phrases without verbs (e.g., “For Home”, “To Warehouse”)
- Repeating elements that depend on their surroundings
Without understanding the context, an LLM can generate a “formally correct” but unnatural or incorrect translation. Thanks to the graph and proper context transfer, Multify avoids these errors.
🔝 What's the Difference for SEO?
In addition to the quality and accuracy of translation using AI models, there is also a significant difference in the technical implementation of a multilingual website, which greatly affects search engine rankings. The fact is that website translation using Google Translate or Yandex Translate, performed after the page loads in the browser, these translations are done client-side and do not contribute to SEO optimizationwhere the application came from.
Search engines do not index translated content, created using automatic tools without human editing, as it is considered automatically generated content.
Search engines do not index translated content, created using automatic tools without human editing, as it is considered automatically generated content.
"Google не индексирует переведённый контент, созданный с помощью Google Translate, что ограничивает видимость вашего сайта на международных рынках."
→ Source: Auris AI [my translation]
Thus, for effective SEO optimization of a multilingual website it is recommended to use server-side solutions, which provide search engines with access to translated content.
🚀 Claude — Best Translation Quality
Currently, Multify uses Claude 3.5 Haiku — this LLM shows the best translation quality for CIS languages: Kazakh, Uzbek, Ukrainian, Romanian, Azerbaijani, Kyrgyz, Armenian, Tajik, Belarusian, Turkmen.
Despite the high cost of Claude compared to other AI models, thanks to its own architecture and the use of unlimited servers, Multify offers:
💸 Competitive Price
🥇 Highest Quality Among Tilda Solutions
🌐 Support for Complex Languages and Regional Variants
🎯 Summary: How It All Works Together
- The page is broken down into logical chunks
- Each chunk gets its own context — text before and after
- A graph is formed, to quickly determine the vicinity during updates
- The model receives the necessary context and produces a coherent, accurate translation
As a result, you get:
✅ Multilingual website without duplicates
✅ Translation that reads naturally
✅ Improved SEO tags and meta tags
✅ Flexibility and scalability without manual routine
✅ Translation that reads naturally
✅ Improved SEO tags and meta tags
✅ Flexibility and scalability without manual routine